1 Intro
Tower for a security system, weather station, internet and comms antennas
1.1 Schematic
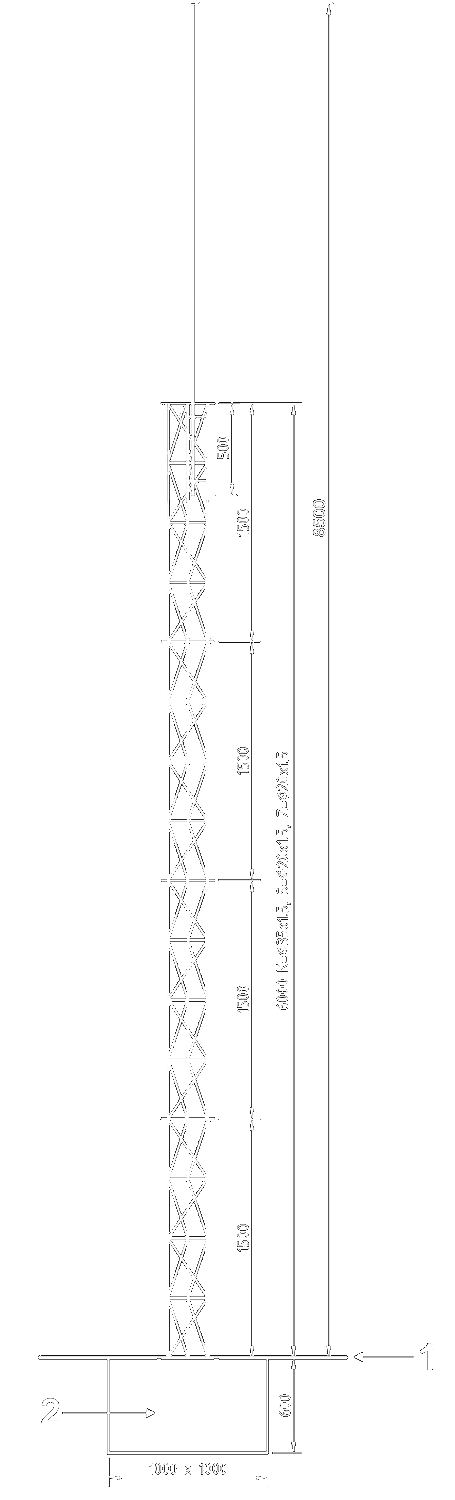
1.2 Specifications
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Height of the mast | 8.5 m |
| Number of sections | • 4 pcs - Truss Mast, |
| • 2 pcs - Pipe Mast | |
| Wall thickness | 1.5 mm |
| Material | Aluminum |
| Construction | Truss of triangular cross-section: |
| 250 x 250 x 250 mm | |
| Supporting pillars | Aluminum tube Ø 35 mm |
| Main features | • The lack of guy-wires |
| • MK-1.5/POD base application enables laying | |
| a mast | |
| • Possibility of entering the assembled mast | |
| by a person weighing up to 100 kgs with | |
| winds up to 5 m/s | |
| • Possibility of transport in the trunk of a | |
| passenger car | |
| • Dimensions of the product after packing | |
| enable sending it by courier across Europe | |
| Weight | • 4 x 5.05 kg - Truss Mast |
| • 2 x 0.72 kg - Pipe Mast | |
| • 1.56 kg - Pipe Clamp OR3-50W6 | |
| • 3.01 kg - Mast base | |
| • 1.6 kg - Anchor for concrete | |
| Guarantee | 2 years |
1.2.1 Pic

2 Wind Load Calculations
2.1 Comparison Graphs
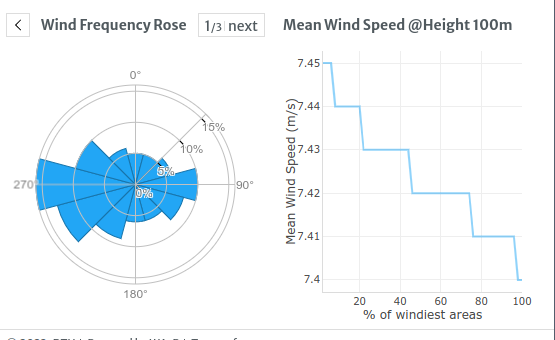
Poland
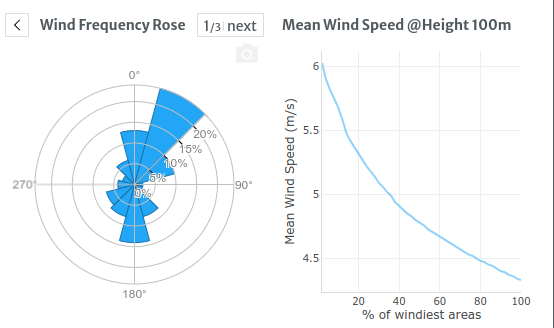
Evia
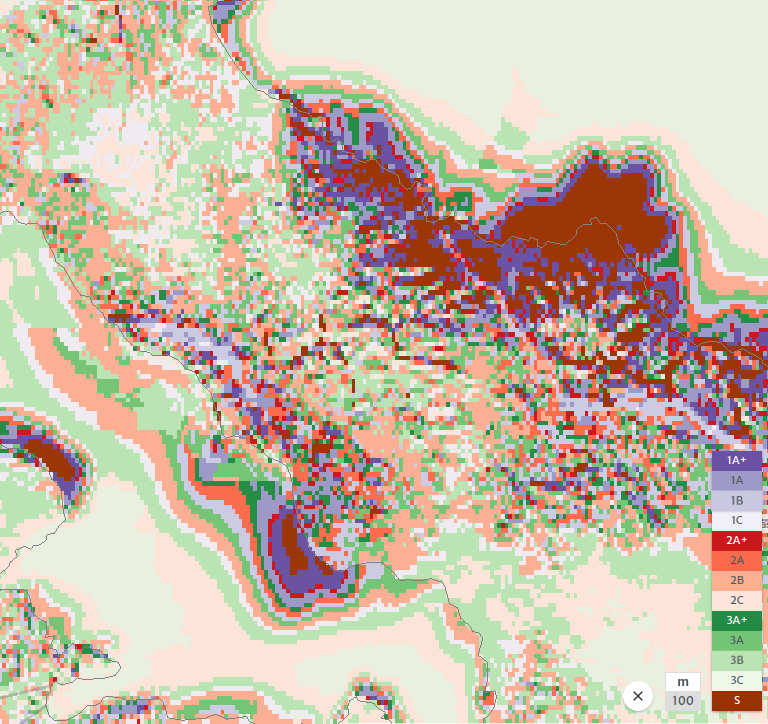
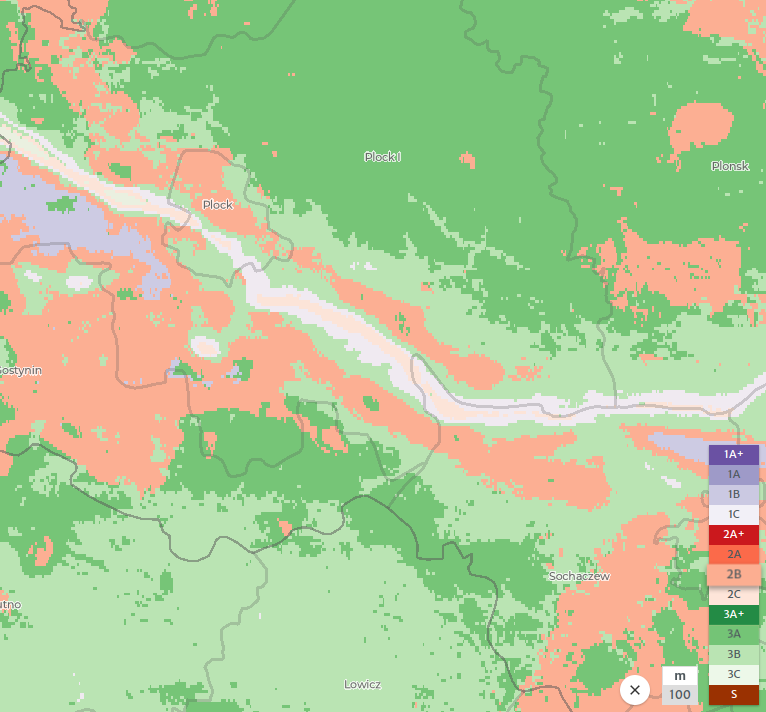
2.2 Comparing Data
2.2.1 IEC data for Evia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEC_61400 (downloaded Evia IEC class data + wind data in qgis) We are around IEC IIB or IIA (Eu Wind Data)
- 8.5 metres per second (31 km/h; 19 mph) avg yearly
- with extreme 50 year gust 59.5 metres per second (214 km/h; 133 mph)
checking IEC data for Poland there are areas with IEC A1 but most of it is 3A etc
- 10 metres per second (36 km/h)
- with extreme 50 year gust 70 metres per second (250 km/h)
2.2.2 EUROCODE comparison
They are claiming the tower is good for Poland wind zone 1 which according to this is
Poland
- Fundamental Basic Wind Velocity: vb,0 = 22.00 m/s
- Basic Velocity Pressure: qb = 0.30 kN/m2
Evia
- Fundamental Basic Wind Velocity: vb,0 = 33.0 m/s
- Basic Velocity Pressure: qb = 0.68 kN/m2
2.2.3 DONE What is Fundamental Basic Wind Velocity?
- Mean wind speed: Average speed over specific duration (10 minutes in this case).
- 10m above ground level: Standard height for measuring wind speed in meteorology.
- Open country terrain: Type of terrain with little to no obstructions to wind flow.
- Return period of once every 50 years: Indicates the wind event’s recurrence interval. In this case, the Vb0 represents the 10-minute mean wind speed expected once in 50 years.
2.2.4 DONE EUROCODE vs IEC differences?
according to EUROCODE Polish tower is not good for Evia at all according to IEC Polish tower is amazing for evia.
how come?
Mismatch due to different nature and aims of the two codes.
- Eurocode (EC): Part of a framework aimed at standardizing structural codes across Europe. EC wind load calcs based on static wind load.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Global organization focusing on electrical, electronic, and related technologies standards. IEC’s focus on dynamic wind loads, appropriate in contexts such as wind turbines.
Different approaches result in different zone classifications and corresponding figures. EC and IEC not necessarily comparable despite both dealing with wind loads and zones.
For your case, best route might be to use sparser EC data as a baseline and refine with more granular IEC data, in consultation with a qualified structural engineer if needed.
3 Notes
- Price: 1200 EUR
- Truss Mast Height: 6m
- Pipe Mast Height: 2.5
- Truss of triangular cross-section : 250 x 250 x 250 mm
3.0.1 Installation example
3.0.2 Shop Links
https://shopdelta.eu/truss-pipe-mast-mkr-8-5ct_l2_p8756.html
3.0.3 Spec
https://shopdelta.eu/pdf.php?page=shop/datasheet&product_id=8756
https://shopdelta.eu/pdf.php?page=shop/instruction&product_id=8756
DONE Wind loads?
There is no data in the spec, need to contact the shop to confirm, preliminary research done
TODO Foundation Dimensions?
There is no data on this in the spec, wtf?
3.1 Other links
3.1.1 QUADRO HEAVY SELF-STANDING TOWER 1000, 5000 eur
Interesting 1x1x10m tower with internal ladder
https://revse.com/self-standing-aluminium-lattice-tower/quadro-heavy-self-standing-tower-1000.html
3.1.2 ALUMINIUM FREE STANDING TOWER H:10M, 2574 EUR
Aluminum tower, special folding S500 series with a height of 10 meters. Its main advantage is a very compact package that facilitates shipment
3.1.3 Rest
weirdly cheap https://revse.com/lattice-masts/tower-kits/tower-ready-kit-5-2m.html
3.2 Notes
- check radome for sat dish
- autonomous security system above?
- cam protector half sphere made out of transparent plastics available on amazon
3.3 expo tower
